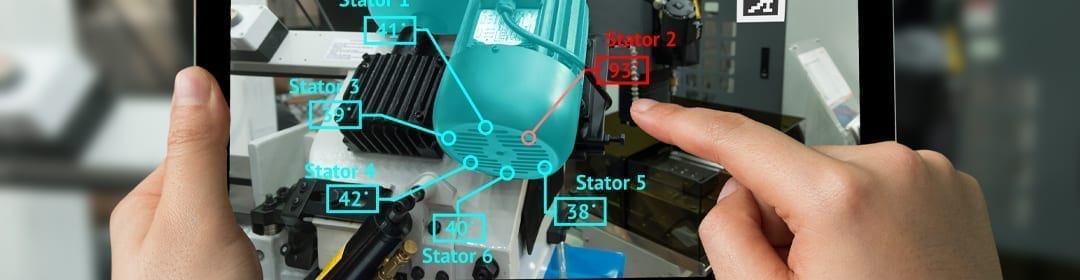
Industrial augmented reality (AR), which involves the use of specialized goggles, glasses or smartphone apps to overlay digital information onto a plant worker’s real-life view, can help increase productivity, efficiency and safety on the manufacturing floor.
Not to be confused with virtual reality (VR), AR technology produces statistics, calculations and other information to give workers increased understanding of their actual surroundings.
Augmented reality has many applications for the industrial sector and manufacturing companies. From MRO to training programs, these use cases aren’t as far off as you might think.
AR is quickly becoming recognized as a helpful tool for manufacturers and not just a toy for consumers.
Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality vs. Mixed Reality
First, it’s important to understand the subtle differences between augmented, virtual and mixed reality. Each type of technology interacts differently with physical and digital space.
Virtual reality (VR) immerses the user completely in a digital world. Virtual reality is all-or-nothing; once you put on the googles, the real world disappears. VR can be helpful for training and creating prototypes, but it would be dangerous to use in an active environment like a manufacturing floor.
Augmented reality (AR), on the other hand, superimposes digital information onto your view of the real world. Because AR remains rooted in what’s happening around you, it can be used for many day-to-day tasks in industrial and manufacturing settings.
Mixed reality is a combination of virtual and augmented reality, allowing interactions between digital and physical elements. Mixed reality technology is still in the early stages of development and adoption, so it is not widely available for industrial applications.
6 Augmented Reality Industrial Applications
1. Product design and development
Concepting and prototyping can be time-consuming and resource-intensive tasks. With AR, engineers can create digital overlays to see what features will look like next to objects in the real world.
Augmented reality provides visibility into the final product throughout the design phase, so you can make changes and improvements at a very low cost.
2. Maintenance and repair
One of the most interesting industrial applications for augmented reality is in the realm of MRO. With AR systems, a technician with expert knowledge does not need to be physically on-site to perform maintenance.
The expert can give step-by-step instructions to anyone with an AR headset, circling important objects and walking them through the process.
Augmented reality systems can also display helpful information about equipment, including operation times, date of last service, potential points of failure and more.
This data can inform preventive and predictive maintenance efforts. It also allows operators to identify and fix issues faster, reducing downtime and associated costs.
3. Training programs
While the real-time capabilities of AR are helpful, augmented reality isn’t limited to live interactions.
You can record training modules that help manufacturing employees learn to complete their task using an AR headset. This is beneficial for complex tasks that are difficult to explain and comprehend using a standard video or text format.
Augmented reality also allows you to train hands-on learners in their preferred learning style at scale. You only need to record the training module once, rather than repeating it for every individual.
4. Assembly
Next, with AR sensors and immediate data analysis capabilities, employees can gain additional insight into complicated tasks and free up their hands to work faster.
This is especially true with assembly. AR systems can overlay blueprints or simple assembly instructions, placing renderings of bolts, cables and part numbers in an employee’s direct line of sight.
This on-the-job task guidance can help decrease training time and minimize assembly errors.
5. Quality control
Since visual inspection of products is a key step in ensuring product quality, the quality control process is unlikely to be completely automated anytime soon.
While human interaction is still needed, augmented reality can improve the process by providing quick access to information.
A quality control technician wearing AR glasses can quickly get details about defective product components and specifications, reducing the amount of time needed for visual inspection.
6. Order picking
Finally, augmented reality can provide easy access to data about warehouse inventory.
Workers can quickly see where products are located and receive navigation to that area of the warehouse. Once they arrive, they can quickly assess inventory levels and estimated order pick times.
All this information improves efficiency because the worker doesn’t need to remember it in their head or continually reference a database on a computer.
The Future of Augmented Reality for Industrial Settings
Since AR lives at the cusp of a new wave of technological advancement, some of the most exciting applications probably haven’t been invented yet.
However, current augmented reality technology for industrial applications still holds great potential for vastly improving productivity and reducing costs.
This article was originally published on February 19, 2020. It was updated and republished on April 14, 2021.
Related articles
Predictive vs. Preventive vs. Condition-based: The 3 Types of Proactive Maintenance
Replacing Old Switchgear Systems: 6 Benefits of Installing New Equipment